Summary
US hospitals and home-care teams now juggle data silos, paperwork that eats cents of every dollar, and record turnover among doctors, nurses, and caregivers. This article lays out eight pressure points like data fragmentation, revenue leakage, caregiver burnout, and staffing gaps, sharing how each one drains time or cash. It also highlights key Healthcare CIOs challenges and shows how early wins with AI in healthcare and agentic AI hint at practical fixes that reclaim clinical hours, speed payments, and steady the workforce.
America’s healthcare bill keeps climbing, yet the day-to-day experience inside clinics and homes feels under-resourced.
In 2023, national health spending had already reached $4.9 trillion, equal to 17.6 percent of GDP, and the share is still inching up. Patients see new buildings and apps, but behind the scenes many teams fight the same old bottlenecks.

These cracks in data, dollars, and staffing weaken everything from preventive visits to complex surgeries.
Early pilots suggest that well-targeted AI in healthcare—think ambient note-taking, predictive scheduling, real-time claims checks, and other caregiver burnout solutions—can relieve some of the load. The sections that follow unpack where the pain is sharpest before we outline, in a later article, how AI can begin to ease it.
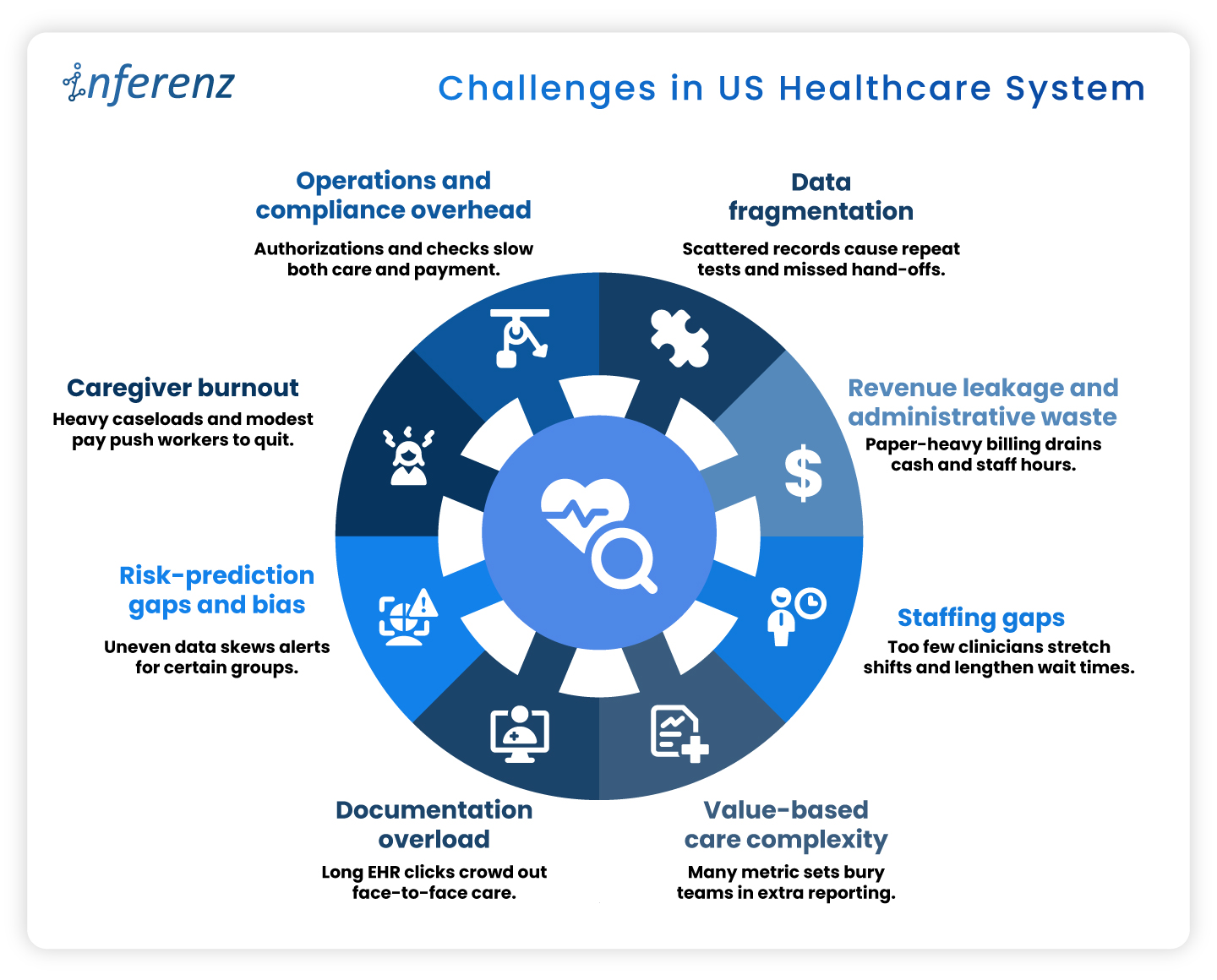
1. Data Fragmentation
Fragmented electronic records drive at least $200 billion a year in repeat labs, imaging, and other avoidable services. Patients often move between dozens of disconnected systems, and prior tests rarely follow them, leading to duplicate records too.
Among chronically ill Medicare beneficiaries, those in the most‐fragmented quartile run $4,542 higher annual costs and show more preventable hospitalizations than peers with integrated care. Scattered data undermines diagnosis accuracy, pushes redundant work onto staff destroying caregiver connect. You need a handy dedupe AI tool to avoid patient representation and other AI solutions to stop inflated claims that payers later dispute.
2. Revenue Leakage and Administrative Waste
Hospitals run sophisticated clinical services, yet their business offices often look like paper factories. Prior authorizations, claim edits, and duplicate data entry push invoices back for revision and restart the payment clock. Each rework touches coders, billers, and case managers, draining time that could fund patient-facing roles.
One hard number shows the scale: administrative costs now consume about 40 percent of every hospital dollar spent. When almost half the budget never reaches a bedside, leaders have less room to raise wages, buy new diagnostic tools, or expand rural outreach. The cycle feeds on itself: tight margins lead to leaner billing teams, which can increase denials and stretch accounts-receivable even further. News flash: Efficient revenue cycle management services are the need of the hour!
3. Staffing Gaps
Clinical talent has become the scarcest supply in health care. Retirement-age physicians leave faster than residency slots can refill them, and many younger clinicians choose outpatient or telemedicine roles over hospital call schedules. Nurses face similar pressures, with heavy workloads and limited autonomy pushing them toward travel contracts or careers outside medicine.
The Association of American Medical Colleges warns that the United States could be short as many as 86,000 physicians by 2036. Staff shortage drives the system: wait times lengthen, overtime soars, and remaining staff shoulder extra shifts that speed burnout. For home-care agencies, thin rosters translate to missed visits and lost revenue when referrals must be declined.
4. Value-Based Care Complexity
Linking payment to outcomes sounds simple on paper. In practice, every bonus program carries its own data dictionary, audit trail, and submission portal. Teams juggle dozens of Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial contracts, with different look-back periods and attribution rules.
A landmark Health Affairs study found that physician practices sink about 15 hours per doctor each week into collecting and reporting quality metrics, at an annual cost of $15.4 billion nationwide. That is nearly two working days lost to spreadsheets instead of patient counseling or chronic-care planning. The hidden toll is morale: clinicians see quality work as vital, yet they resent duplicative forms that rarely inform real-time decisions.
5. Documentation Overload
Electronic health records promised efficiency but often delivered extra clicks. Templates proliferate, alerts pop up mid-exam, and note bloat forces physicians to scroll through pages of copied text. After clinic closes, many providers log back in from home to finish charts.
Recent research in JAMA Network Open shows primary-care doctors spending a median 36.2 minutes in the EHR for a 30-minute visit. Such documentation overload squeezes appointment slots, delays billing, and fuels frustration on both sides of the screen. Patients wait longer for follow-up calls, and clinicians lose family time, accelerating departure from full-time practice.
6. Risk-Prediction Gaps and Bias
Predictive models guide everything from sepsis alerts to readmission flags, but they inherit the blind spots of the data beneath them. If some groups receive fewer tests, algorithms may label truly sick patients as low risk. Poor signal leads to poor care and potential legal exposure.
A University of Michigan study found that white emergency patients received up to 4.5 percent more diagnostic tests than Black patients with similar presentations. When such data bias in records train AI, the resulting tools underrate risk for under-tested populations and can widen outcome gaps that policy aims to shrink. Predictive staffing in healthcare suffers on this front, a lot.
7. Caregiver Burnout
Home-care aides, nurses, and therapists anchor community health, yet their jobs are physically taxing and poorly paid. Heavy caseloads, unpredictable schedules, and emotional labor drive many to exit the field. Agencies then scramble to recruit replacements, often at higher cost, instead of looking for effective caregiver burnout solutions.
Industry tracking shows caregiver turnover in home care reached 79.2 percent last year. Nearly four in five workers left within twelve months, erasing institutional knowledge and breaking continuity for vulnerable clients. High churn forces agencies to reject new referrals or rely on overtime, compounding stress for those who remain.
8. Operations and Compliance Overhead
Regulatory safeguards protect patients but can swamp providers in forms. Prior authorization, eligibility checks, and electronic visit verification (EVV) each add data steps between care and payment. Staff must phone insurers, upload documents, and wait for green lights before proceeding.
An American Medical Association survey reports that 94 percent of physicians say prior authorization delays access to needed care. These holdups lead to cancelled procedures, rehospitalizations, and frustrated families. Organizations also pay for the privilege: teams spend hours per week on approvals that rarely change clinical decisions, yet every stalled claim inflates days-cash-on-hand risk.
Why AI Sits at the Pivot Point
Taken together, the pressure points above form a single pattern: vital clinical minutes vanish into data hunts, billing loops, and staffing scrambles. Every home care agency especially need to take note that
- When intake stalls, a patient’s first touch runs late.
- When documentation drags, the visit itself shrinks.
- When claims wait in limbo, funds for follow-up dry up.
The system feels these shocks end to end.

Agentic AI offers a direct counterweight because it slots into each phase of care:
- Start of care: Conversational intake tools collect histories, verify coverage, and label high-risk cases before the first appointment. Clean data flows forward instead of fragmenting at the gate.
- Point of care: Ambient notetaking, real-time risk scores, and predictive staffing engines give clinicians more face time and safer shift patterns. The visit becomes richer while administrative drag drops.
- Post care: Automated coding, denial prediction, and longitudinal analytics speed payment and flag avoidable readmissions through AI-based patient engagement software. Dollars return sooner, lessons cycle back into quality plans, and staff energy stays on patients rather than portals.
Advanced analytics, ambient clinical documentation, predictive scheduling, and automated claims triage each target the pain points above. Early results such as Agentic AI scribes cutting note-taking time and fairness-aware models closing bias gaps, hint at relief.
The next article will map problem-solution pairs in depth; for now, it is enough to see that AI, applied responsibly, can clear data blockages, shorten queues, and free human attention for care itself.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does AI in healthcare cut the daily paperwork load?
Smart tools pull data from multiple EHRs, fill forms, and flag missing fields in real time. Clinicians review and sign instead of typing from scratch, easing the healthcare administrative burden without changing clinical workflows.
2. What makes agentic AI different from other healthcare AI systems?
Agentic models work as goal-driven “mini agents.” They read context, decide next steps, and update tasks across apps—ideal for EHR integration or claim edits that need many small, fast decisions.
3. Can automation really fix revenue leaks?
Yes. Modern revenue cycle management services combine denial prediction with inline coding checks. They stop errors before submission, improve first-pass rates, and speed cash back to hospitals.
4. How do hospitals use artificial intelligence scheduling to close staffing gaps?
Algorithms study census trends, PTO requests, and overtime patterns. The result is predictive staffing healthcare rosters that match demand hour by hour, which lowers burnout and agency-nurse spend.
5. What role does ambient clinical documentation play at the point of care?
Voice AI listens during the visit, writes concise notes, and posts them to the chart. Providers keep eye contact with patients and note lag drops—often by more than half.
6. How can a home care agency tackle 79 % caregiver turnover?
Platforms that blend caregiver burnout solutions with fair route planning let aides pick shifts, cut idle travel, and get instant mileage pay. Happier schedules improve 90-day retention.
7. Why should payers and providers care about AI for prior authorization now?
Automated PA engines read clinical notes, fill payer forms, and chase status updates. They shorten approval windows from days to minutes, freeing staff for higher-value tasks and improving patient engagement software scores.
8. What do top healthcare AI companies focus on when starting a project?
They begin with data quality. Clean data feeds every downstream model, whether for infection alerts or remote-care analytics. A solid pipeline beats flashy features that sit on bad inputs.